The Bitcoin halving cycle occurs about every four years. Bitcoin has demonstrated patterns across previous four-year cycles, and many believe that the halving can potentially provide investors with some indication regarding price movements.
The Bitcoin halving is an event that takes place approximately every four years. By cutting the supply of new bitcoin entering circulation, the halving has previously demonstrated significant influence over the price of bitcoin, acting as a catalyst for the formation of new, long-term price trends.
The next Bitcoin halving is expected to take place in April 2024, and so it is important to gain a better understanding of the four-year cycle that Bitcoin has experienced since its creation.
Tip: The halving process restricts the introduction of new bitcoin to the circulating supply.
What is the Bitcoin four-year cycle?
Bitcoin miners are required to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and create new blocks on the
However, this reward is cut in half once 210,000 new blocks have been created, hence the name given to the event. Historically, these Bitcoin halvings have occurred approximately every four years.
The Bitcoin halving has previously impacted the price of the cryptoasset, and so crypto investors usually monitor the four-year cycle closely to try and maximise their returns.
Tip: The date of each Bitcoin halving will be impacted by the speed at which new blocks are created.
However, aside from determining the new BTC reward for mining a block, the Bitcoin halving can also impact the price of the cryptoasset. As a result, crypto investors usually monitor the four-year cycle closely to try to maximize their returns.

Stages of the Bitcoin halving cycle
Previous Bitcoin halving cycles have led to significant price increases, so investors typically pay attention to Bitcoin and other cryptoassets in the run-up to the event.
The price of Bitcoin follows different patterns pre- and post-halving. After previous halvings, the price of Bitcoin demonstrated impressive growth in the next 12- to 18-month period. In some of these cases, it reached a new all-time high, as demonstrated in the BTC chart below. This period is referred to as a “crypto bull market”.
After a new all-time high is reached, Bitcoin usually experiences a significant price drop due to a sell-off in global stocks. This period is called a ‘crypto bear market’.
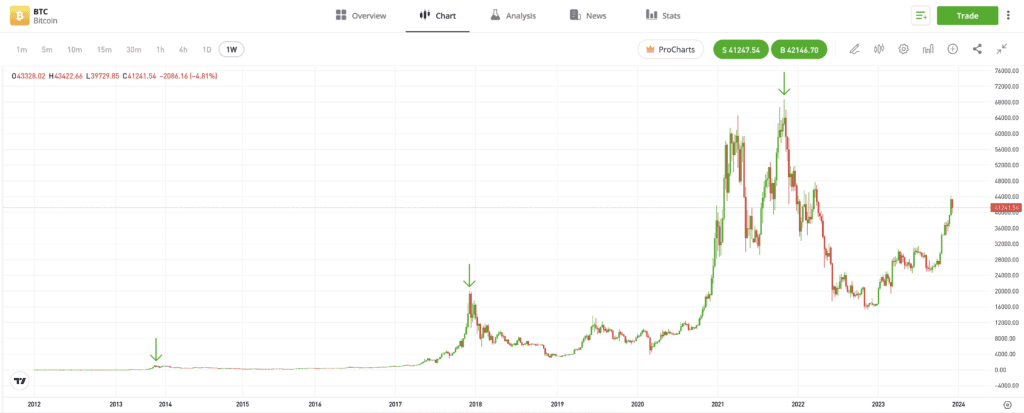
For illustration purposes only. Past performance is not an indication of future results.
Source: eToro
Experienced investors will attempt to buy Bitcoin and other cryptoassets while the prices are low and then sell when their prices are higher. Still, it’s crucial to note that there is no guarantee that the upcoming Bitcoin halving will follow the same pattern as previous four-year cycles.

Bitcoin halving dates history
The Bitcoin halving takes place approximately every four years once the appropriate number of blocks (210,000) have been created.
The dates of previous Bitcoin halving events are as follows:
- November 28, 2012
- July 9, 2016
- May 11, 2020
These dates mark the exact point at which block rewards were reduced by 50%. Still, market conditions varied before and after these specific points in time.
Bitcoin price changes around halving cycles
Historical price data shows that the price of Bitcoin increased between previous halving events. The similarities between past Bitcoin halvings often lead to upcoming halving events generating substantial interest from retail investors, resulting in a surge in trading activity.
This can result in additional price
Tip: Bitcoin price moves can start in the build-up to the next halving event.
What causes bitcoin price changes around halving dates?
There are a range of factors that can influence the price of Bitcoin. The first reason, however, is that the value of Bitcoin — like any other asset — is impacted by supply and
Although this is always the case, market conditions are impacted by upcoming changes to the rewards system within the Bitcoin ecosystem around the time of the halving. The restriction of the supply of new bitcoins into the market causes scarcity and increases demand among traders and investors.
Previous price increases associated with the halving event also indicate an influx of new investors, which further increases the demand for the cryptoasset. Also, retail investors are more likely to start investing in Bitcoin as the media hype around the halving increases. That way, the Bitcoin price will likely go higher.
Historical prices vs future Bitcoin price predictions
Historical price movements can provide insights or predictions into future BTC price movements. However, it’s not only this factor that plays a role, as wider macroeconomic factors also come into play and should be taken into consideration.
Moreover, blockchain technology is still evolving, so despite the patterns highlighted by previous Bitcoin halvings, there is no way to ascertain how the Bitcoin price will react to the next halving event.

Final thoughts
The Bitcoin halving is a relatively straightforward concept that has led to the formation of several patterns throughout the coin’s four-year cycle. Before and after the halving every four years, Bitcoin experiences a renewed interest from retail investors and reduced supply.
Additionally, the coin is hit by historically volatile price movements that typically cause trading volumes and the Bitcoin price to increase around the time of the halving event.
This positive price movement is then followed by a significant price decline, which usually stalls the next Bitcoin halving. Understanding how this cycle works can provide investors with a good basis for their investment decisions. However, it is important to note that previous four-year cycles do not guarantee similar results in upcoming cycles.
Visit the eToro Academy to learn more about Bitcoin and other cryptoassets.
Quiz
FAQ
- Who owns the Bitcoin network?
-
The Bitcoin network is not owned by anyone. It was created by Satoshi Nakamoto, a pseudonymous individual or group, and the ongoing management of the blockchain is carried out by its users. Bitcoin’s Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism enables the network to operate without needing to be overseen by a specific governing body.
- What is Proof of Work (PoW)?
-
Proof of Work is the technique used by some crypto networks, such as Bitcoin, to verify new transactions on a blockchain. Proof of Work is not the only mechanism available for validating transactions, but it is used by Bitcoin to remove third-party intermediaries from the process.
Proof of Work requires significant computational power, as Bitcoin “miners” compete to solve a complex mathematical problem. The successful miner adds a new block to the Bitcoin blockchain and is rewarded with the network’s native cryptoasset — in this case, bitcoin — as a result.
- What are the rewards for mining bitcoin?
-
When a Bitcoin miner validates a new block, they are rewarded with a set amount of bitcoin as a reward, though this reward halves periodically. For instance, after the April 2024 halving, the reward for mining a new block on the Bitcoin network was reduced from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC. A subsequent mining in 2028 will cause a 50% reduction to 1.5625 BTC.
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any financial instruments.
This material has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and has not been prepared in accordance with the legal and regulatory requirements to promote independent research. Not all of the financial instruments and services referred to are offered by eToro and any references to past performance of a financial instrument, index, or a packaged investment product are not, and should not be taken as, a reliable indicator of future results.
eToro makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this guide. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose.


