The term cryptocurrency has become synonymous with bitcoin. Bitcoin is the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalisation and has become the figurehead in a move away from traditional banking systems. Despite its increasing popularity, many don’t really understand what Bitcoin is and what purpose it has.
We explain how Bitcoin works and how it grew to be the best-known cryptocurrency in the world.
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies based on a blockchain, a decentralised digital ledger that records and tracks cryptocurrency transactions. Bitcoin was designed to act as a decentralised alternative to traditional fiat currencies, removing the need for third-party intermediaries.
Bitcoin was not the first digital currency, but it was the first decentralised cryptocurrency to achieve such a level of success.
Tip: When the “B” in Bitcoin is capitalised, the word is referring to Bitcoin as a concept, including the technology, protocol and software behind it. When the “b” in bitcoin is lowercase, it is referring to bitcoin as a unit of currency.

What is bitcoin mining?
“Mining” refers to the simultaneous process of generating new bitcoins and confirming blockchain transactions. To remain decentralised, a blockchain must confirm and validate all new transactions that take place on the network.
Unlike commodities, such as gold, bitcoin mining is completed using computer resources. Those interested in validating the next block of transactions in a blockchain, called validators or miners, are required to solve a complex computational, mathematical problem.
“Hashing” is a method of cryptography that converts data into a unique string of fixed-length text. A hash is like a digital fingerprint. No matter how many times you put the same data through a hash function, you will always end up with the same hash.
Bitcoin miners compete with one another to find the specific hash value generated by cryptocurrency transactions on a blockchain. The first computer (validator) to find the solution is able to validate the next block of transactions in the chain and is rewarded with bitcoin for their efforts.
What gives bitcoin its value?
Despite being created as an alternative to government-backed currencies, bitcoin is not widely used in retail transactions. Unlike other cryptocurrencies, bitcoin is also not backed by a physical asset, like the US dollar. So, why does bitcoin have value?
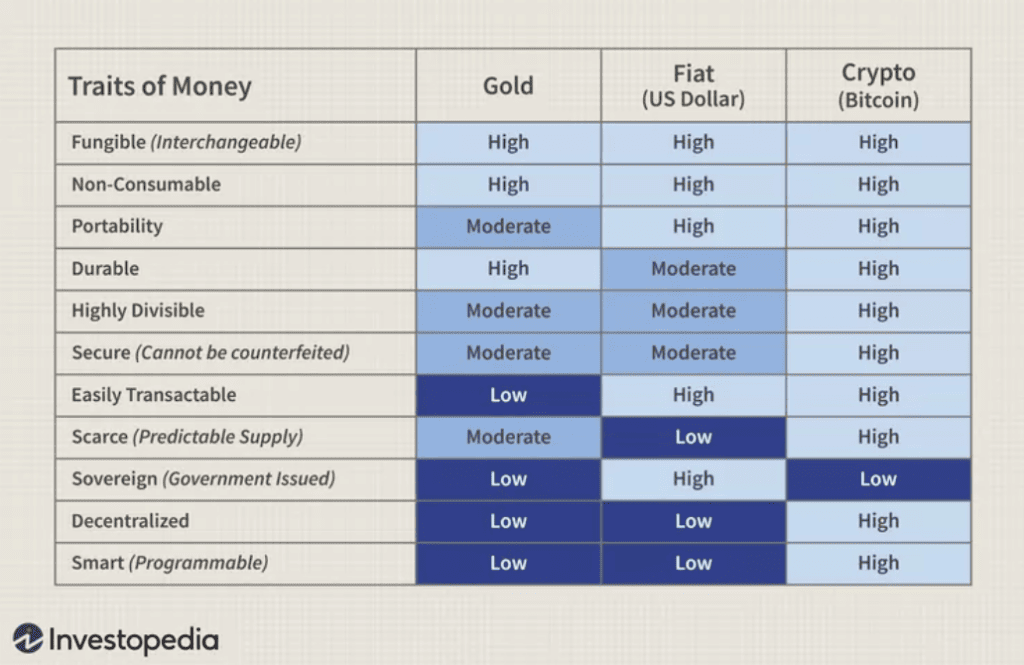
| Scarcity | Whereas fiat currencies can be printed at the will of a government, bitcoin has a total maximum supply of 21 million BTC, making it more similar to a commodity than a traditional currency. |
| Decentralisation | Bitcoin does not need to rely on a centralised party to validate transactions and govern its network. The more users that Bitcoin has, the more secure it becomes, making it an attractive proposition for investors. |
| Divisibility | Bitcoin can be divided into smaller denominations, making it ideally suited for use in transactions, much like fiat currencies. For example, there are 100,000,000 satoshis in every bitcoin. |
| Portability | Cryptocurrencies, including bitcoin, can be transferred via the internet with ease, making them much more portable than other assets, such as commodities. |
| Fungibility | Every bitcoin has the same value as every other bitcoin, regardless of previous ownership or history. This makes them a fungible asset and a suitable store of value. |
| Recognisability | Bitcoin is easily distinguishable from other cryptocurrencies. It has value because of its increasing popularity and the growing acceptance of bitcoin as a method of payment. |
| Transparency | All bitcoin transactions are recorded and accessible on the blockchain, increasing decentralisation and trust in the network. |
What is needed is an electronic payment system based on cryptographic proof instead of trust, allowing any two willing parties to transact directly with each other without the need for a trusted third party.
Bitcoin – A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System

Source: Investopedia
History of Bitcoin
In 2008, a paper called “Bitcoin — A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” was posted on a public forum about cryptography . The paper was posted by Satoshi Nakamoto, a pseudonymous individual or group whose real identity has never been confirmed.
In 2009, Bitcoin was made available to the public, and mining, the process of creating new bitcoins and recording and verifying transactions on the blockchain, began.
Until 2010, bitcoin had only ever been created, rather than traded, meaning that it held no monetary value. A year after it was created, somebody bought two pizzas for 10,000 BTC, finally providing actual value to the cryptocurrency.
Bitcoin was designed to act as a decentralised alternative to traditional fiat currencies, removing the need for third-party intermediaries.
Bitcoin price and forecast for the future
Bitcoin is subject to the same volatility as the rest of the cryptocurrency market, meaning its price fluctuates heavily.
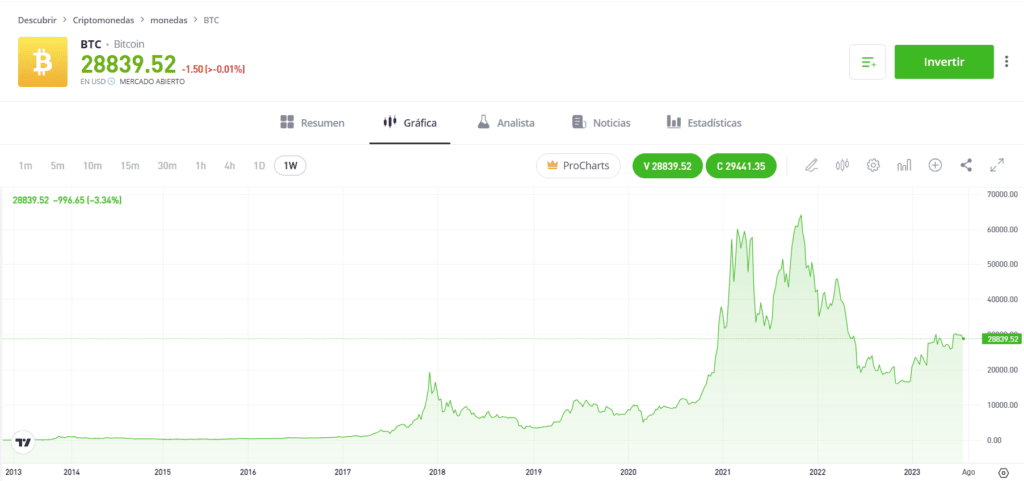
The value of bitcoin hovered between $0 and $30 for a few years after its creation. However, in December 2013, bitcoin demonstrated its incredible volatility, as well as its significant potential as an investment, by trading around $1,200.
The price of bitcoin rose and fell for the next few years, eventually breaking the $2,000 barrier in May 2017 and skyrocketing to over $19,000 in December that same year.
After trading sideways for the next couple of years, the price of bitcoin took off in 2020 and 2021, eventually reaching an all-time high of almost $69,000 in November 2021.
There is no way of accurately predicting the future price of bitcoin. Some believe that bitcoin will continue on a similar trajectory, with the value of BTC continuing to move upwards on average. Others are confident that the price of bitcoin will plateau one day. Regardless, it’s important to do your research and prepare for any eventualities.
Tip: For investors interested in cryptocurrencies, it is worth diversifying your portfolio with a variety of cryptoassets. Investors might also consider investing in altcoins as they offer a higher risk-return potential than bitcoin.
Past performance is not an indication of future results.
Source: eToro
Final thoughts
Bitcoin, alongside other cryptocurrencies, is one of the most controversial technologies to have been developed in recent years. Its price volatility makes it both an attractive but risky proposition for investors. For some, Bitcoin represents more than just an investment, however. It represents an economic shift away from government involvement and a point of central control. Regardless of the reasoning behind it, it’s hardly surprising that many investors are interested in bitcoin as a means of diversifying their portfolio.
Head to the eToro Academy to learn more about bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies, including our Bitcoin Halving Course.
FAQs
- What is Bitcoin halving?
-
The Bitcoin halving, or “the halvening,” is an event that takes place approximately every four years, or more specifically, every 210,000 blocks. The halving event is built into the design of Bitcoin, and reduces the mining rewards — and, therefore, the number of new bitcoins entering circulation — by 50%. The Bitcoin halving made mining bitcoin an attractive proposition in the early days of the network, while helping to maintain its position as a store of value in the future.
- Why is Bitcoin controversial?
-
There is plenty of controversy surrounding Bitcoin and the wider cryptocurrency market. Governments are wary of Bitcoin because it cannot easily be regulated and represents a potential threat to the traditional financial system. Bitcoin’s mining process also requires huge amounts of computational power, leading to significant energy consumption.
- How can I invest in Bitcoin?
-
There are several ways for people to invest in Bitcoin. Buying and selling bitcoin from a cryptocurrency exchange is one potential way to invest in the digital currency. Some investors prefer to use a trading platform that allows them to trade fractional shares of bitcoin, while offering them access to Copy trading, as well as Stop-Loss and Take-Profit features. Alternatively, it is possible to invest in bitcoin using an ETF (Exchange-Traded Fund) that replicates the price of the cryptoasset.
This information is for educational purposes only and should not be taken as investment advice, personal recommendation, or an offer of, or solicitation to, buy or sell any financial instruments.
This material has been prepared without regard to any particular investment objectives or financial situation and has not been prepared in accordance with the legal and regulatory requirements to promote independent research. Not all of the financial instruments and services referred to are offered by eToro and any references to past performance of a financial instrument, index, or a packaged investment product are not, and should not be taken as, a reliable indicator of future results.
eToro makes no representation and assumes no liability as to the accuracy or completeness of the content of this guide. Make sure you understand the risks involved in trading before committing any capital. Never risk more than you are prepared to lose.


